Related topics
▸ Add a maintenance plan
▸ Parts and activities of the plan
▸ Notes and attachments of the plan
▸ Add another maintenance plan as
▸ Edit a maintenance plan
▸ Delete a maintenance plan
▸ Add parts
▸ Edit parts
▸ Delete parts
▸ Copy and paste parts
▸ Insert a maintenance plan within another
▸ Add activities
▸ Edit activities
▸ Frequency of activities
▸ Priority of activities
▸ Duration of the activities
▸ Strike team
▸ Classification of activities
▸ Activities that involve the taking of a measurement (predictive Maintenance)
▸ Procedure to perform the activities
▸ Safety notes, images, and attachments of activities
▸ Requirements to close or include activities in OT
▸ Delete activities
▸ Copy-and-paste activities
▸ Linking maintenance plans
▸ Linking a maintenance plan with activities with the regime of readings
▸ Desligar maintenance plans
▸ Alert computers without linked plan
▸ Alert maintenance plans without assigning it to a computer or location
Introduction to maintenance plans
A fundamental part of the control of the maintenance routine is the formation of plans or routine maintenance.
Plans or routine maintenance are models that contain the information regarding the activities of routine maintenance that must be made to the equipment. The activities of routine maintenance usually consists of actions aimed to prevent failures and are performed in a cyclic way, and repeated with a certain frequency.
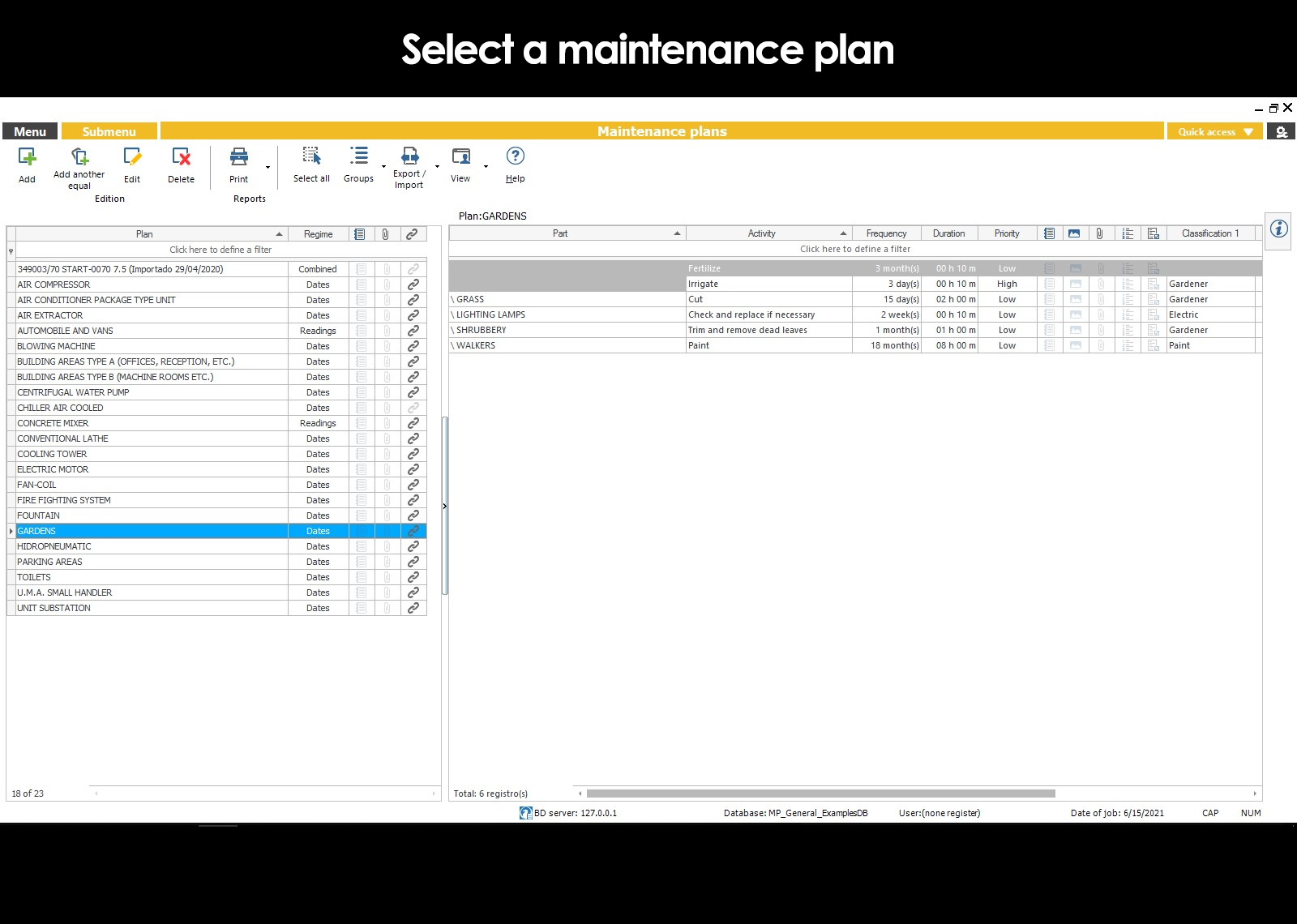
Basic elements of a maintenance plan (Parties, activities, and frequency)
A maintenance plan is composed of three basic elements:
| MAINTENANCE PLAN | ||
|---|---|---|
| PARTS | ACTIVITIES | FREQUENCY |
| The parts of the computer. | The routine activities that must be made to each of the parties. | The frequency with which they should be performed each of the activities. |
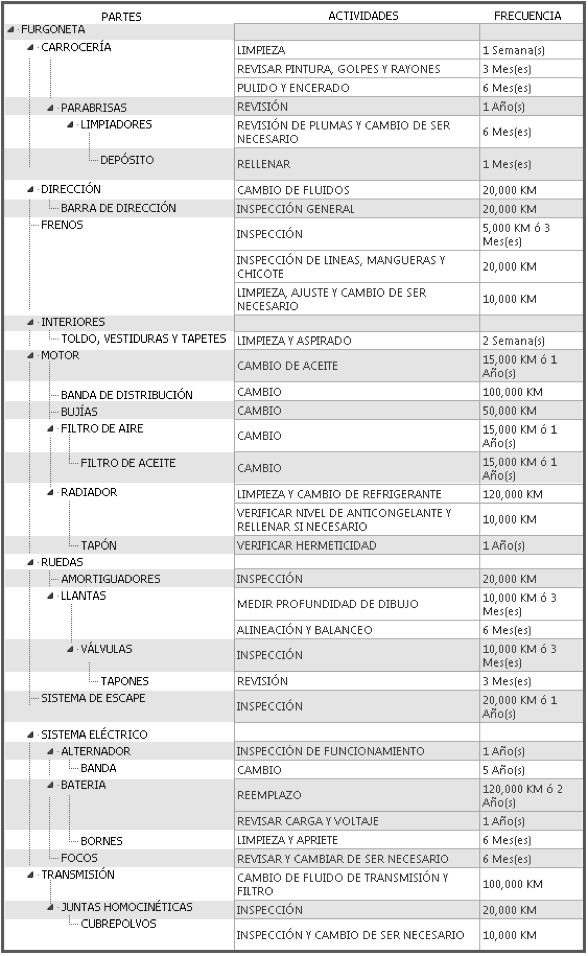
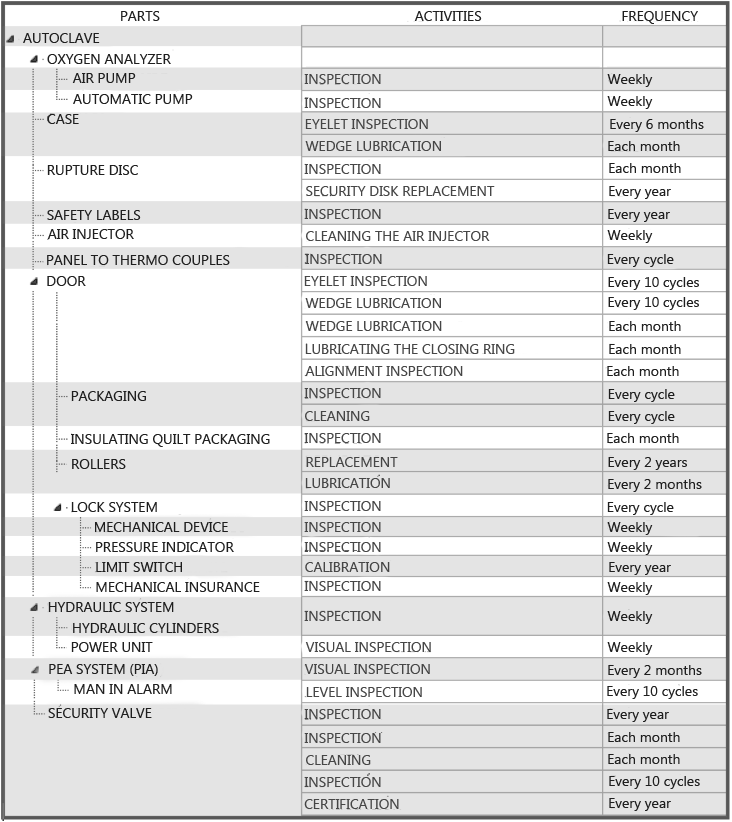
To define the parts of a computer, the system handles a structure forest.
|
Example:
|
Rate based on datesIn a maintenance activity controlled based on dates, the frequency with which it should be done the activity is set in function of the elapsed time. (For example, every day, every week, every 15 days, every 3 months, every 2 years, etc) Frequency based on readingsIn a maintenance activity is controlled on the basis of reading, the frequency with which it should be done the activity is based on the use of the equipment. (Example, kilometers traveled, hours of use, units produced, number of ignitions, cycles, etc) Mixed frequencyIn a maintenance activity mixed, the frequency with which it should be done the activity is based on the use of the equipment or time, whichever comes first. (Example, every 15,000 miles or 12 months, whichever occurs first) |
A maintenance plan is composed of three basic elements:
| MAINTENANCE PLAN | ||
|---|---|---|
| PARTS | ACTIVITIES | FREQUENCY |
| The parts of the computer. | The routine activities that must be made to each of the parties. | The frequency with which they should be performed each of the activities. |
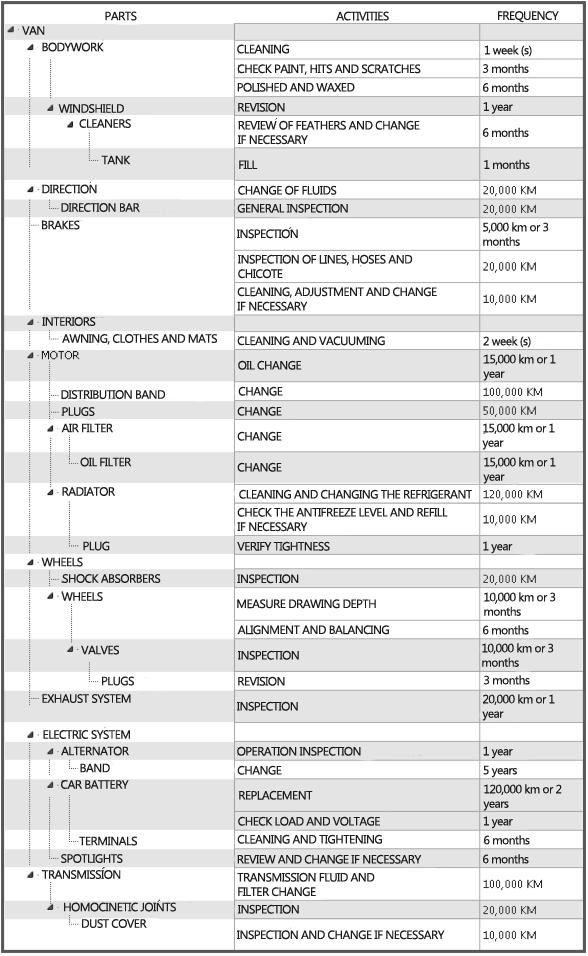
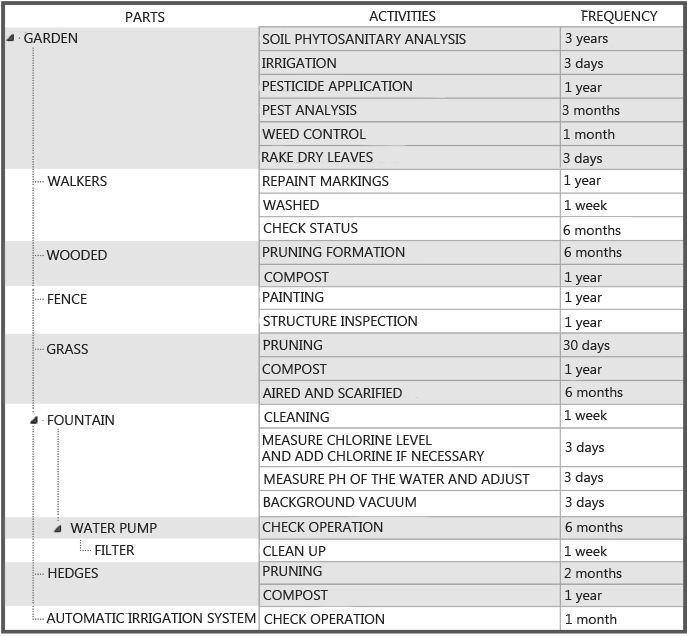
| To define the parts of a computer, the MP operates a structure forest.
|
Example:
|
Rate based on datesIn a maintenance activity controlled based on dates, the frequency with which it should be done the activity is set in function of the elapsed time. (For example, every day, every week, every 15 days, every 3 months, every 2 years, etc) Frequency based on readingsIn a maintenance activity is controlled on the basis of reading, the frequency with which it should be done the activity is based on the use of the equipment. (Example, kilometers traveled, hours of use, units produced, number of ignitions, cycles, etc) Mixed frequencyIn a maintenance activity mixed, the frequency with which it should be done the activity is based on the use of the equipment or time, whichever comes first. (Example, every 15,000 miles or 12 months, whichever occurs first) |
The user is the one who structure the plans of maintenance of your equipment based on your experience or recommendation of the manufacturers of the same
Therefore, the system is an application program that can be implemented in any company, regardless of the types of equipment or locations with the one that counts. We can create plans for routine maintenance and equipment to locations, or real estate.
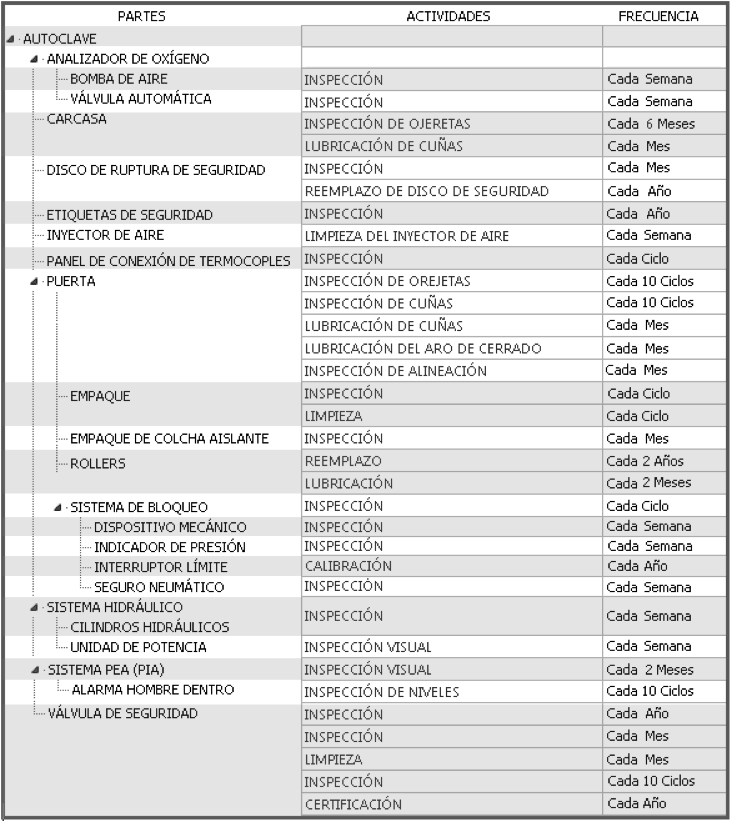
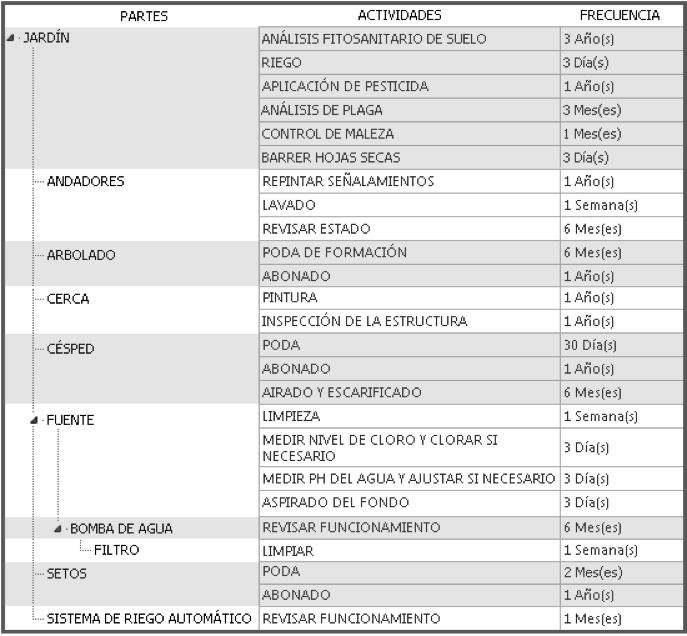
Examples of maintenance plans:
Planning of preventive maintenance generates savings of capital, guarantees a longer time of service, facilities, equipment and machinery, contributing value to the company and higher reliability
Can't find the answer to your doubts or questions?
Additionally, we offer training courses
Our flexible options of online training and face-to-face will provide you with all the knowledge necessary to understand and implement your software maintenance.