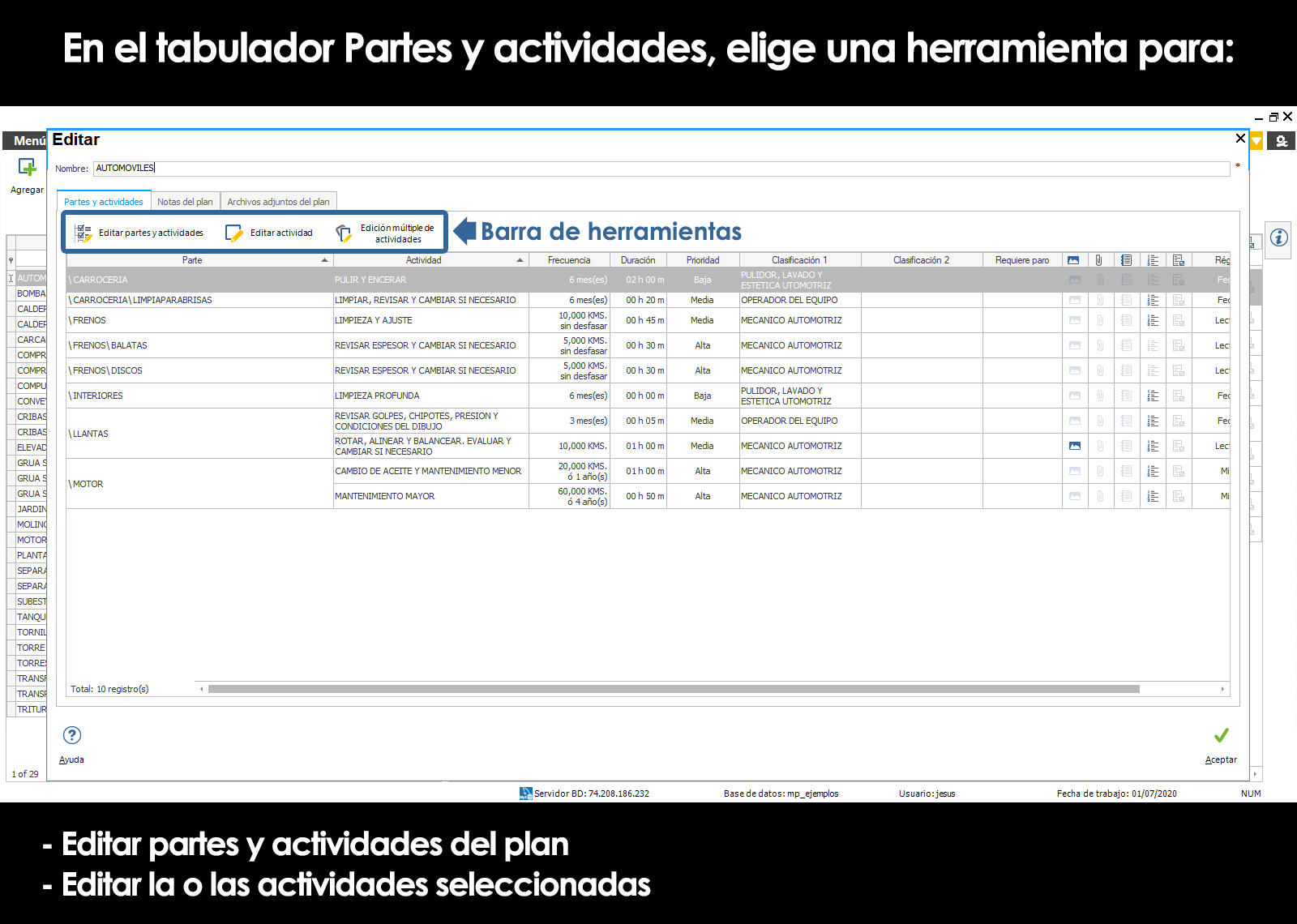
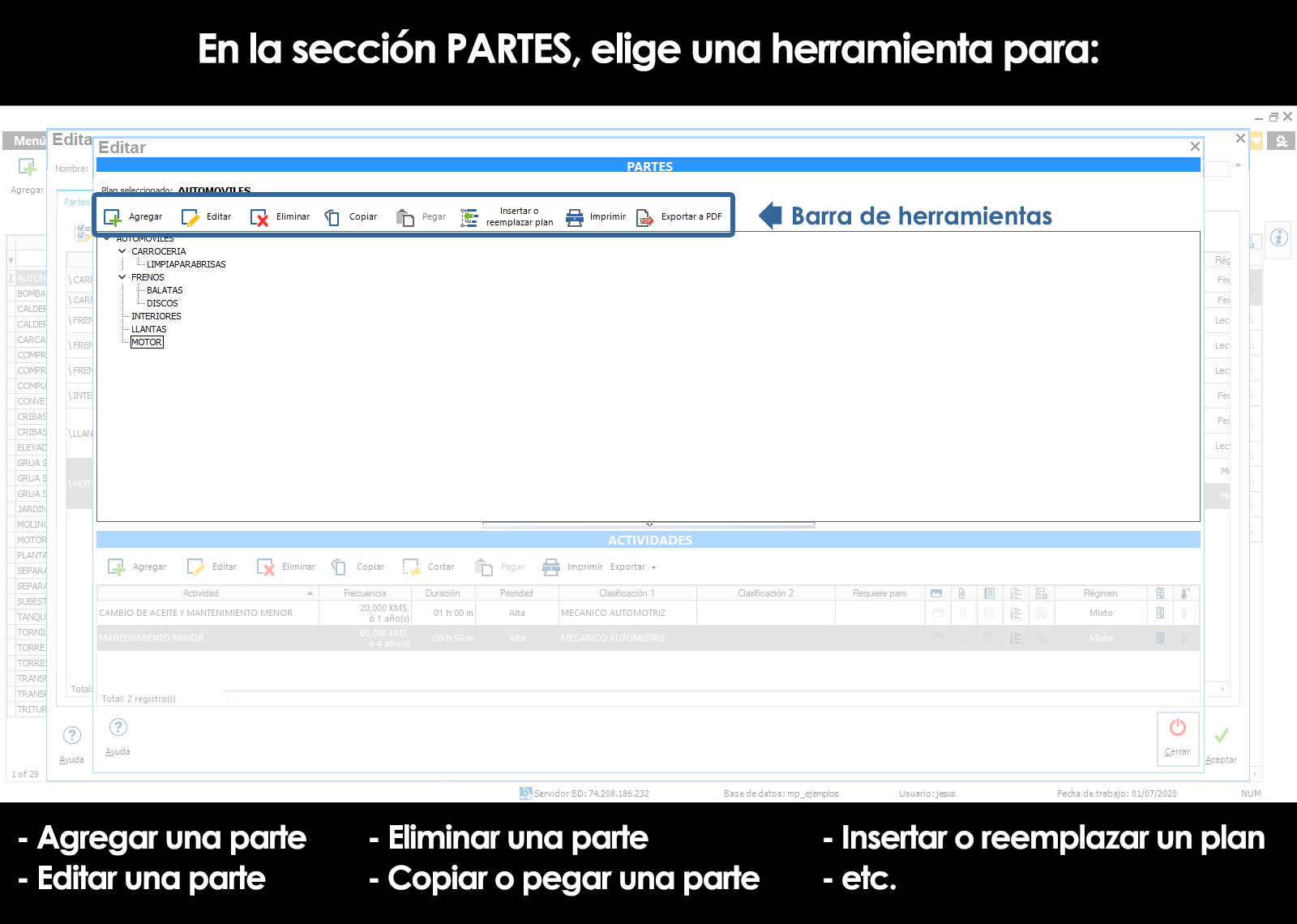
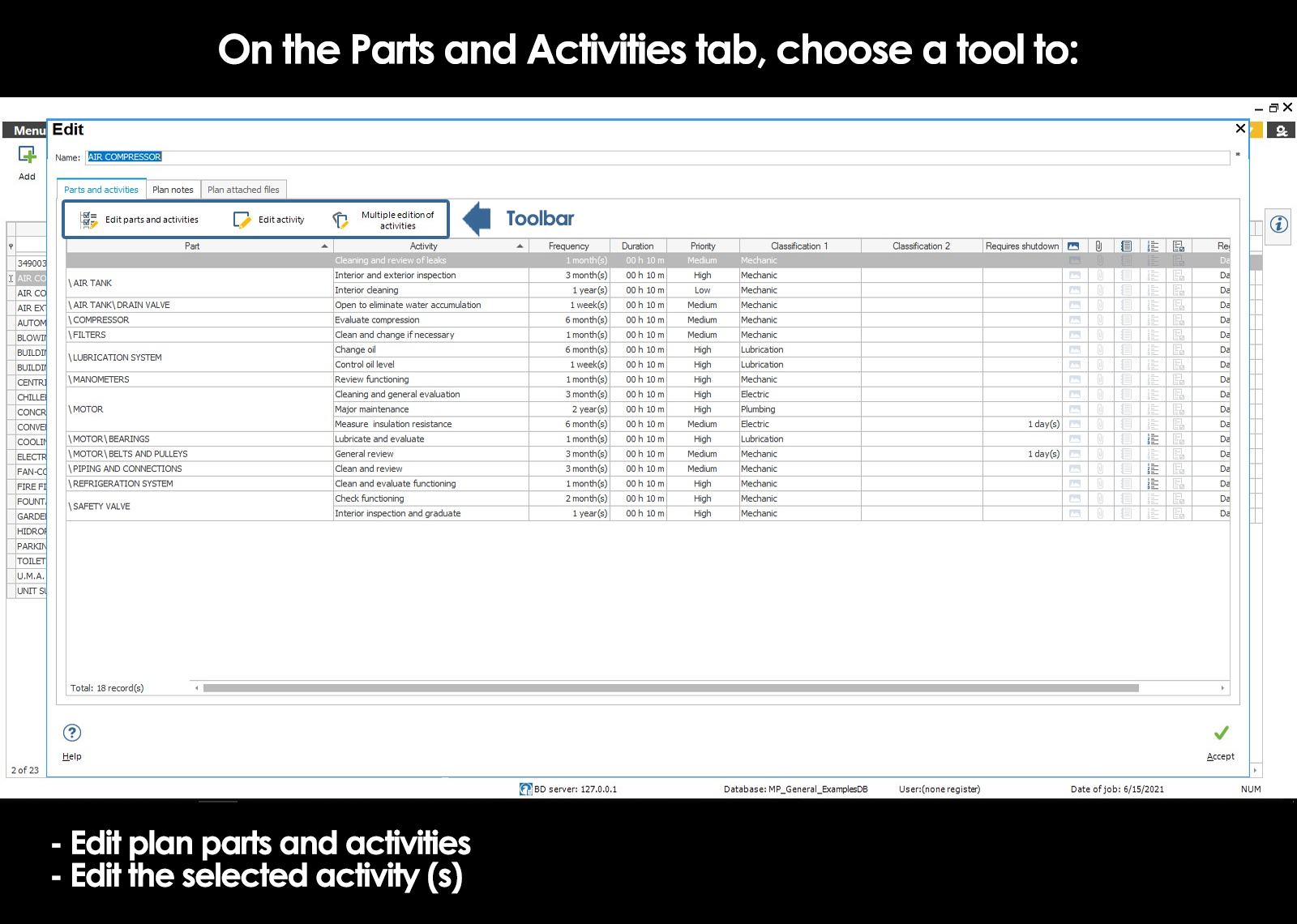
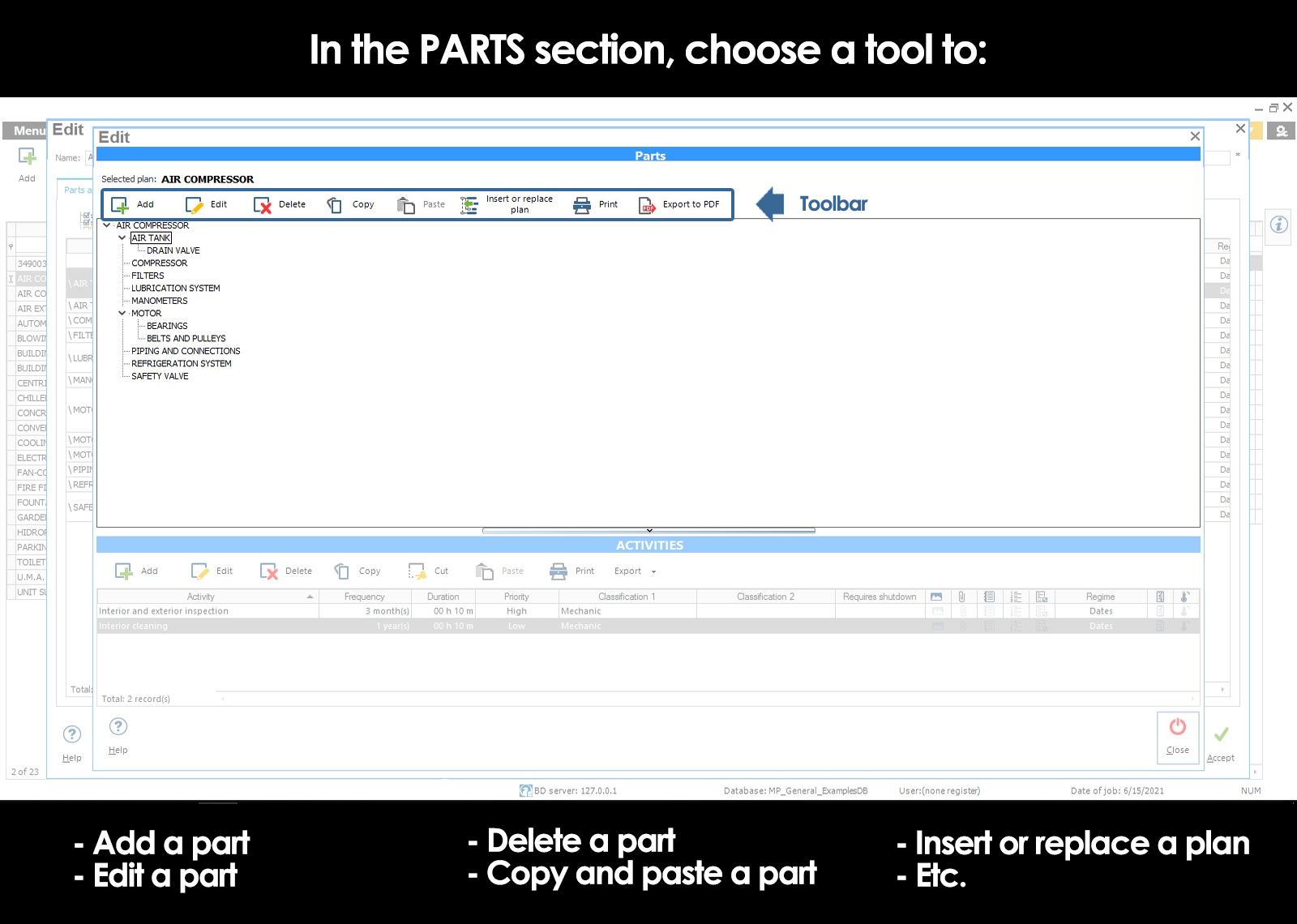
Add parts
Edit parts
Remove parts
Copy and paste parts
Insert a maintenance plan within another
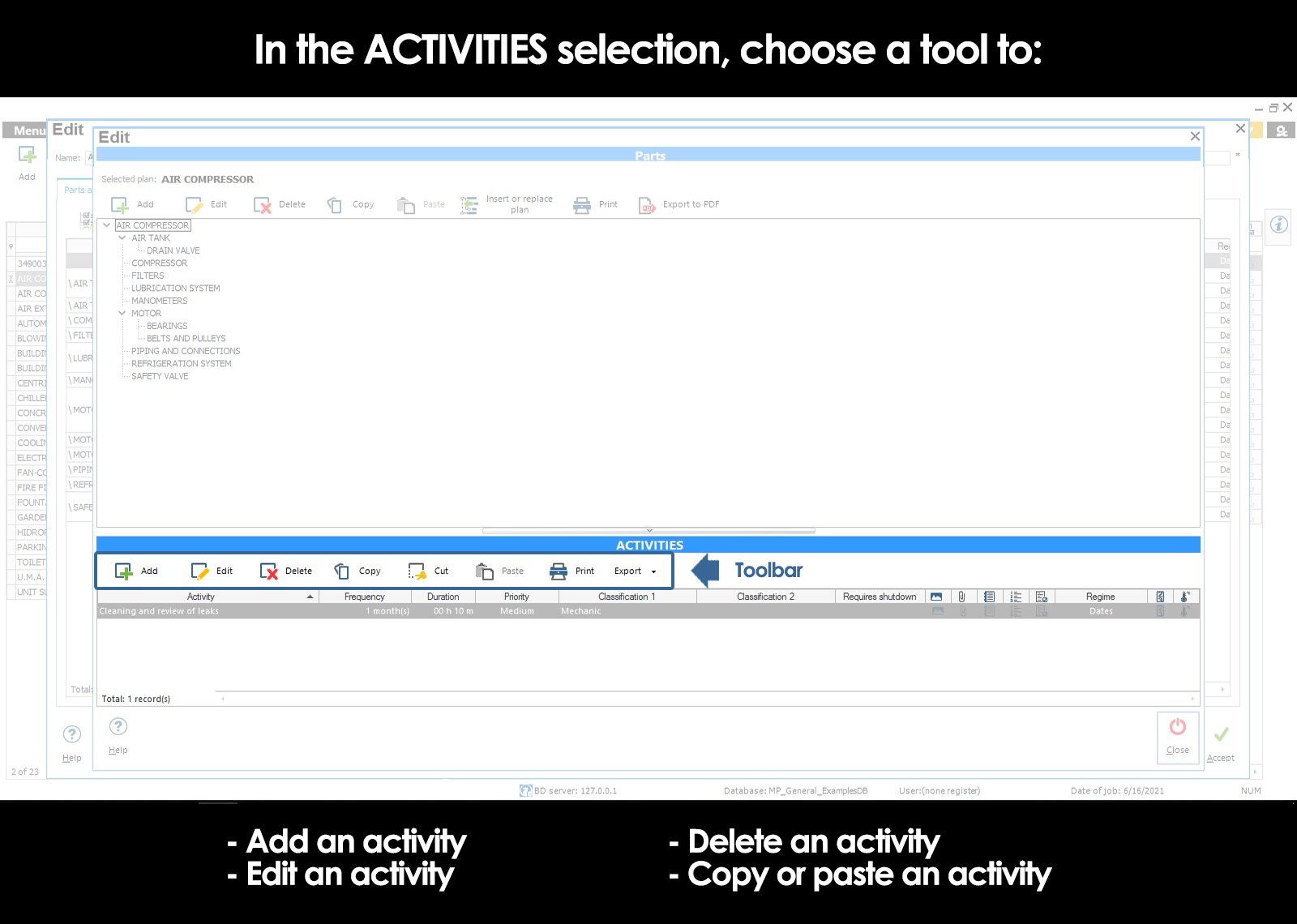
Add activities
Edit activities
Frequency of activities
Priority activities
Duration of the activities
Shutdown the computer
Classification of activities
Activities that involve the taking of a measurement (predictive Maintenance)
Procedure to perform the activities
Safety notes, images, and attachments of activities
Requirements to close or include activities in OT
Delete activities
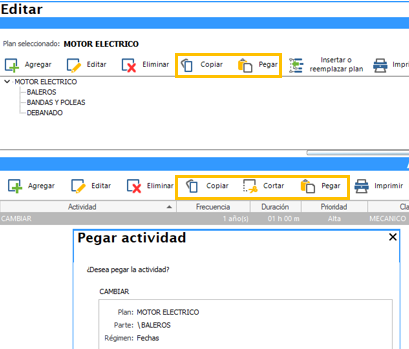
Copy-and-paste activities
Related topics
▸ Introduction to maintenance plans
▸ Basic elements of a maintenance plan (Parties, activities, and frequency)
▸ Submenu of the catalog maintenance plans
▸ Add a maintenance plan
▸ Parts and activities of the plan
▸ Notes and attachments of the plan
▸ Add another maintenance plan as
▸ Edit a maintenance plan
▸ Delete a maintenance plan
▸ Linking maintenance plans
▸ Linking a maintenance plan with activities with the regime of readings
▸ Desligar maintenance plans
▸ Alert computers without linked plan
▸ Alert maintenance plans without assigning it to a computer or location
Add parts
To record the parts of the maintenance plan press tool Add within the section “Parts” of the window Parties and activities.
The system uses a structure brandishing to define the parts of the computer. As are registering the parties, it provided a tool with which you can position in the party or desired level of the tree.
Remove parts
To delete the selected part, press the tool Delete within the section “Parts” of the window Parties and activities. When you perform this action, you will lose all the sub-parts, and related activities at the removed part.
Copy and paste parts
The System allows copy and paste them including their sub-parts, and related activities. This function is very useful when a computer has multiple equal parts with sub-parts, and/or similar activities. We can even perform this action from one plan to another.
Insert a maintenance plan within another
The tool Insert or replace plan allows you to insert a given plan high above in a selected part of the plan of routine maintenance that is being edited, or replaced.
To use select the part you want to replace, subsequently click on the tool Insert or replace planopens a window in which you should select the desired plan and choose the action to perform, either insert or replace.
For example:
| Inserting or Replacing a maintenance plan | ||
|---|---|---|
| You have the maintenance plan AIR COMPRESSOR |
You want to insert or replace the part MOTOR | Plan to insert or replace ELECTRIC MOTOR |
 |
 |
 |
| Result | |
|---|---|
| When you Insert the maintenance plan | When to Replace the maintenance plan |
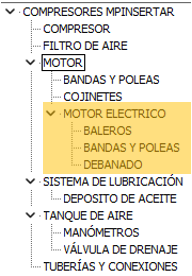 |
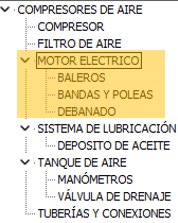 |
| Inserting or Replacing a maintenance plan | ||
|---|---|---|
| You have the maintenance plan AIR COMPRESSOR ALTERNATIVE |
You want to insert or replace the part MOTOR | Plan to insert or replace ELECTRIC MOTOR GE |
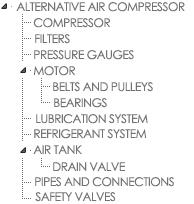 |
 |
 |
| Result | |
|---|---|
| When you Insert the maintenance plan | When to Replace the maintenance plan |
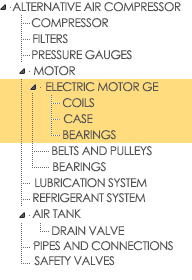 |
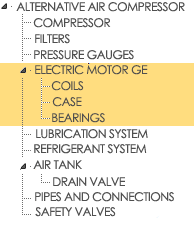 |
Add activities
As mentioned above, the activities are related to a part of the team or the entire team. Before you add an activity, we must select the part of the computer-related activity. If there is a specific part, then we can relate the activity at the root level, to refer to the entire team.
To register for an activity, press the tool Add within the “Activities” section of the window Parties and activities.
Edit activities
To modify the information of an activity, press the tool Edit within the “Activities” section of the window Parties and activities.
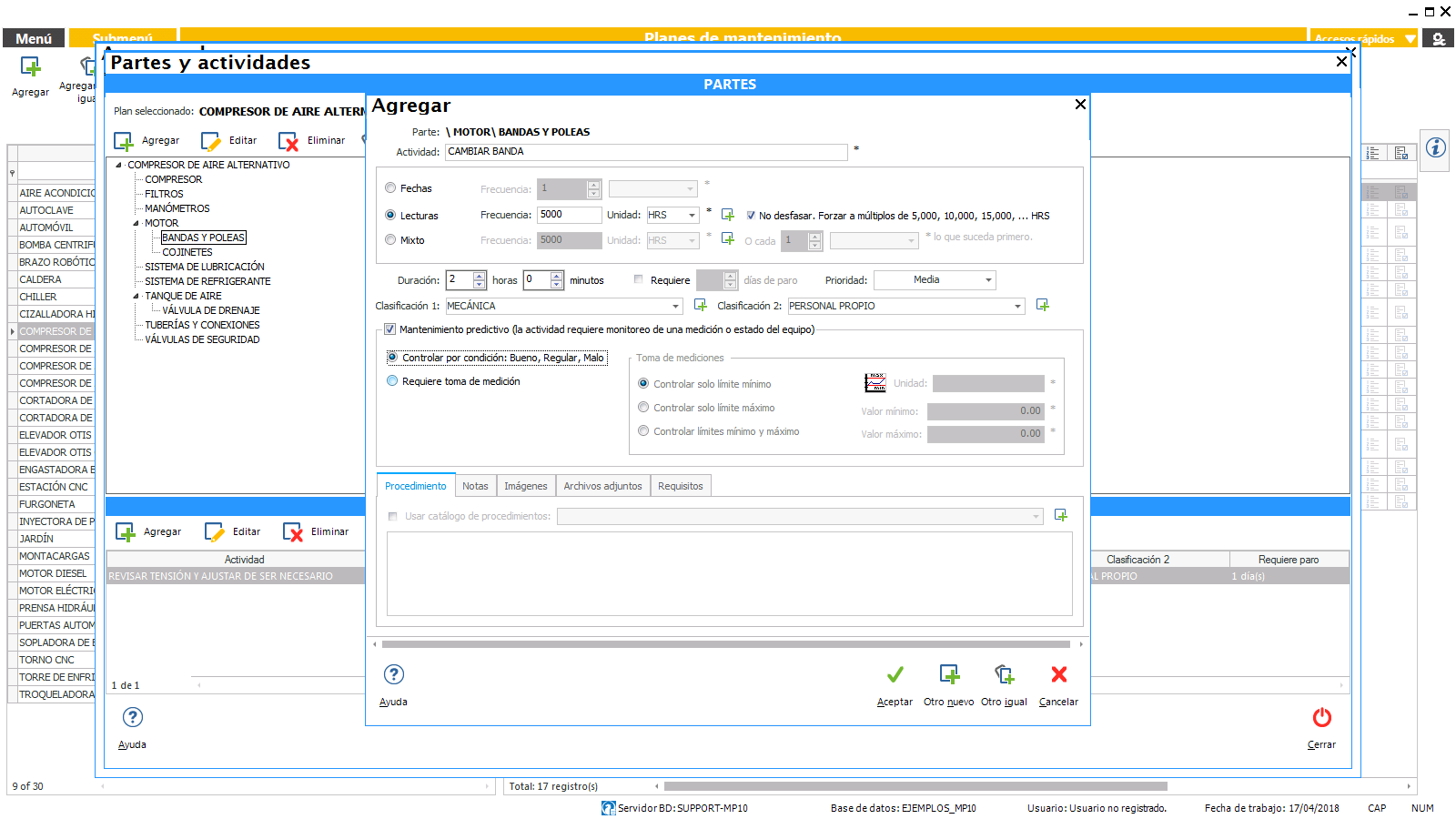
The first thing we need to do is assign a name to the activity and to establish the frequency with which it should be done. Below, we describe each of the fields and options that are provided in the system to document the activities.
Frequency of activities
You can set the frequency of the activities of the following form:
- Rate based on dates
In a maintenance activity controlled based on dates, the frequency with which it should be done the activity is set in function of the elapsed time. (For example, every day, every week, every 15 days, every 3 months, every 2 years, etc) - Frequency based on readings
In a maintenance activity is controlled on the basis of reading, the frequency with which it should be done the activity is based on the use of the equipment. (Example, kilometers traveled, hours of use, units produced, number of ignitions, cycles, etc)Option not to skew the readings and force multiples (Often on the basis of reading)
When there is a delay or an advance in the realization of a controlled activity for reading, the MP will adjust or will automatically run the reading for the next maintenance.
For example:
Suppose an activity that is performed with a frequency of 5,000 Km, and the work is physically made up to 5,700 Km with a backlog of 700 KM. By default, the MARKER will schedule your next maintenance for the 10,700 Km away, next to the 15,700 Km and so on, keeping a gap as a result of the delay.
When you activate the check-box Do not delay [ ], indicates to the MARKER that you must keep exact multiples of the frequency. For example, 5,000 Km, 10,000 Km, 15,000 Km, and so on, regardless of the delays that may occur.
- Mixed frequency
In a maintenance activity mixed, the frequency with which it should be done the activity is based on the use of the equipment or time, whichever comes first. (Example, every 15,000 miles or 12 months, whichever occurs first)
Priority activities
Indicates the importance of the activity. At the time of generating work orders, we will be able to set filters to issue in the first instance, for example, the activities of higher priority.
It is possible to set the priority level of the activities such as low, medium or high.
Duration of the activities
In the duration field is set to the estimated time that is required to perform the activity. We will be very helpful to distribute the workload among the maintenance personnel.
As you are assigning work orders to each person, the MP presented to us in a graph the sum of the estimated time of the activities assigned to each worker, and help us to optimize the distribution of the workload.
Shutdown the computer
Check this box when a maintenance activity required to stop the production in order to do it, indicating the number of days estimated that the equipment will be out of service due to maintenance activity. Activities that require the arrest will be reflected on the board of major shutdowns, helping to plan for the arrest of the equipment in advance.
Classification of activities
The system allows you to assign two classifications are independent of the maintenance activities.
An example of classification is recommended based on the specialty required to perform the activity.
For example Classification 1:
- Tecnico Electromecanico
- Instrumentalist
- Lubricator
- Technical maintenance to cooling
For example Rank 2:
- Painting
- Mechanical
- Electric
- Instrumentation
In this case, at the time of generating work orders, you can group the activities and issue work orders separated by specialties, or type of work.
At the time of editing an activity, the rankings are selected from a list of catalog auxiliary classifications. If the desired rating is not yet registered, it is possible to register on line by clicking on the icon To add to the catalog located to the right of the fields of Classification 1 and 2.
You can also add and edit the catalog of classifications from the module Catalogs auxiliary the Main menu.
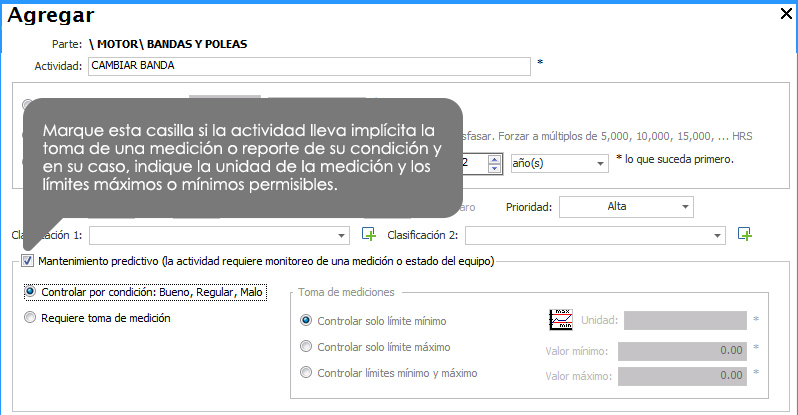
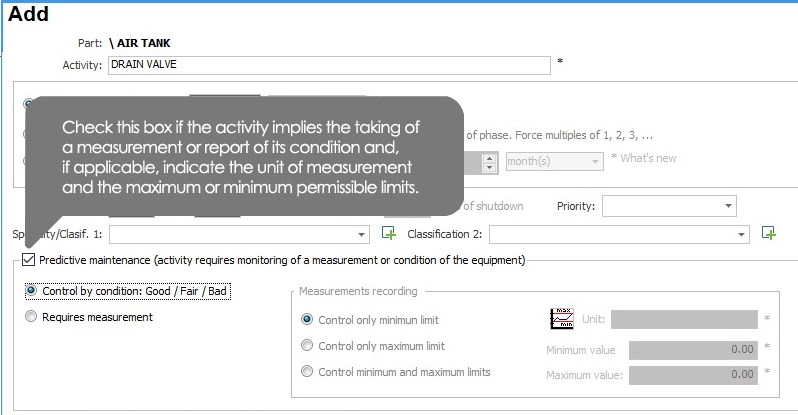
The activity requires monitoring of a measurement or condition of the equipment (predictive Maintenance)
There are maintenance activities that involve the taking of a measurement, such as, for example, to measure temperature, vibration, thickness, insulation resistance, amperage, etc. Or simply, review activities in which they want to monitor the condition of the equipment or any of its parts, leaving a record on whether the equipment or a part of the team are found in good, fair or poor condition at the time of the review.
Procedure to perform the activity
The procedure is a text field that allows you to describe the way of carrying out the work.
Since the procedures are often used in a repetitive way, the system allows you to save them within a Catalog auxiliary proceduresthat will allow us to select them without having to re-type it each time.
To edit the information of the procedures, this can be done from the screen capture of the activity and if you wanted to modify the content of a procedure previously saved in the catalog, you must do so from the module Catalogs auxiliary the Main menu.
In many occasions it is convenient to use the text field procedure to describe a set of activities that can be implied in the main activity.
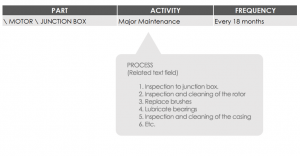
Suppose as an example, an activity of major maintenance of the engine. Such activity, implicit in the implementation of several activities. For practical purposes, it is easier to register a single activity, that is to say, major maintenance of the engine and in the text field of procedure, to make a complete description of the activities implied, and the way of performing them.
Example:

In the example shown above, the control and management is simple because at the time indicate that the activity has been completed, it is sufficient to “palomear” just an activity, or the activity of major maintenance.
The disadvantage is that since it is a text field, so they don't have individual control over each of the activities described in the procedure.
Now note that the maintenance schedule shown below is equivalent to the maintenance plan is shown above. The basic difference is that in this second option, the activities implied in the major maintenance are broken down. This second option allows the control and programming of the activities implied in the major maintenance independently, to sacrifice the simplicity that it offers the option mentioned above.
| PART | ACTIVITY | FREQUENCY |
|---|---|---|
| \ENGINE\CONNECTION BOX | Inspection | Every 18 months |
| \ENGINE\ROTOR | Inspection and cleaning | Every 18 months |
| \ENGINE\BRUSHES \ENGINE\BEARINGS \ENGINE\HOUSING |
Replace Lubricate Inspection and cleaning |
Every 18 months Every 18 months Every 18 months |
Finally, the decision to choose one or the other will depend on how you want to handle the user.
In many occasions it is convenient to use the text field procedure to describe a set of activities that can be implied in the main activity.
Suppose as an example, an activity of major maintenance of the engine. Such activity, implicit in the implementation of several activities. For practical purposes, it is easier to register a single activity, that is to say, major maintenance of the engine and in the text field of procedure, to make a complete description of the activities implied, and the way of performing them.
Example:
In the example shown above, the control and management is made easier at the time to indicate to the MARKER that the activity has been completed, it is sufficient to “palomear” just an activity, or the activity of major maintenance.
The disadvantage is that since it is a text field, so they don't have individual control over each of the activities described in the procedure.
Now note that the maintenance schedule shown below is equivalent to the maintenance plan is shown above. The basic difference is that in this second option, the activities implied in the major maintenance are broken down. This second option allows the control and programming of the activities implied in the major maintenance independently, to sacrifice the simplicity that it offers the option mentioned above.
| PART | ACTIVITY | FREQUENCY |
|---|---|---|
| \ENGINE\CONNECTION BOX | Inspection | Every 18 months |
| \ENGINE\ROTOR | Inspection and cleaning | Every 18 months |
| \ENGINE\BRUSHES \ENGINE\BEARINGS \ENGINE\HOUSING |
Replace Lubricate Inspection and cleaning |
Every 18 months Every 18 months Every 18 months |
Finally, the decision to choose one or the other will depend on how you want to handle the user.
Safety notes, images, and attachments of the activity
- Notes
In addition to the description of the activity, the user can document notes for each activity. - Images
The system also allows for document images illustrating for example a procedure, lubrication points, etc, related to the activity, which may be printed with the work order. - Attachments
To complement the documentation of the activity, it is possible to append to the activity attachments of the type-PDF, DOC, CAD, etc, as they could be manuals, technical specifications, drawings, etc
Requirements to close or to include the activity in an OT
At the time of editing an activity, the system allows the user to optionally indicate in your case the following requirements, by ticking the appropriate box:
- Requires prior authorization before generating the OT [ ]
The activities that have the appropriate box checked, may only be included in a work order through an authorization. The authorization consists of typing a key of a supervisor authorized at the time of generating the OT. - Requires Vo. Bo. to close the OT [ ]
Once an activity, the user must indicate that the work has been done so that the system re-schedule the next date for when you need to be performed again. - The activities that have the check box “Require Vo. Bo. to close the OT “ may only be closed or to be marked as done prior authorization from a supervisor authorized to do so. The authorization consists of typing a key of a supervisor authorized at the time of mark as done the activity.
- Other requirements [ ]
In the case of other requirements, there is a catalogue auxiliary requirements. In the catalog, the user will be able to document other requirements, which will be printed at the time of printing the work order. For example, permission to work at height, need special equipment, security, etc
Delete activity
To delete the selected activity, press the tool Delete within the section “Parts” of the window Parties and activities. Will not eliminate the activity if it is included in a work order.
Can't find the answer to your doubts or questions?
Additionally, we offer training courses
Our flexible options of online training and face-to-face will provide you with all the knowledge necessary to understand and implement your software maintenance MP.